About Anioma
Anioma is the indigenous name and collective identity of the Igbo-speaking communities that occupy the Northern part of present-day Delta State.
A Shared Identity
Igbo-speaking communities bound by common ancestry, language, and cultural heritage.
A Defined Homeland
Communities historically rooted in Delta North (Anioma region) of present-day Delta State.
A Collective Aspiration
Documented pursuit for equity, recognition, and the creation of Anioma State.
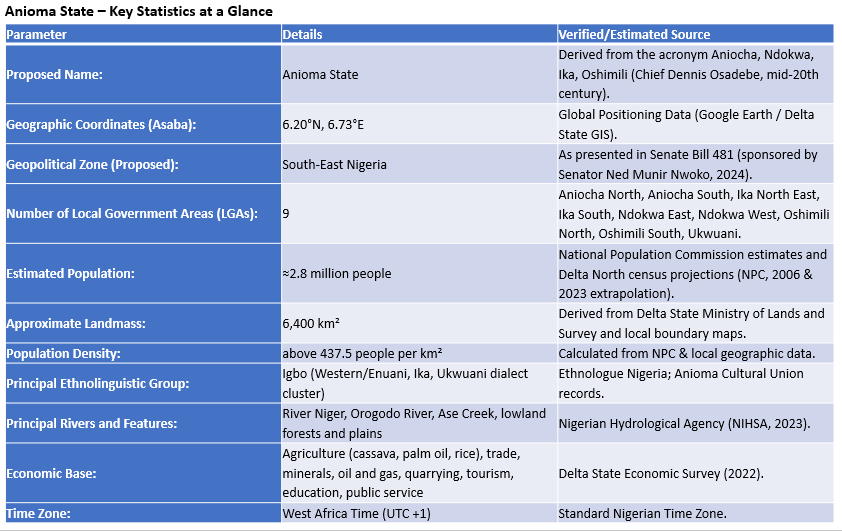
Anioma is the indigenous name and collective identity of the Igbo-speaking communities that occupy the Northern part of present-day Delta State. The name “Anioma” is an Igbo phrase meaning “good land” and an acronym drawn from Aniocha, Ndokwa, Ika and Oshimili. It was coined in the 1960s by Chief Dennis Osadebe the first and only Prime Minister of the Mid-Western Region, and popularized in the mid-20th century by regional leaders who sought a single, dignified identity for the western Igbo groups of the Niger’s west basin.
Anioma lies on the western floodplains and uplands of the Niger River, a strategic geographic corridor that has long connected the eastern and western halves of southern Nigeria. The region’s landscape is enriched by waterways such as the Orogodo River, Pontu River in Kwale, Ase Creek, and several lowland plains that support its thriving agricultural and ecological systems. Asaba, the Delta State capital, is currently Anioma’s primary urban centre. Asaba sits roughly at 6.20°N, 6.73°E latitude and 6.73°–6.75°E longitude, anchoring Anioma as the riverine gateway between eastern and western Nigeria. This location makes the region strategically important for inland trade, transport and cross-river cultural links.
The Anioma landscape blends riverine wetlands and fertile agricultural plains with modest highlands and important market towns that historically connected inland trade routes. Anioma is majorly an agrarian region. Anioma’s fertile environment promotes its diverse economic activities such as agriculture, trade, quarrying, tourism, education, and public service. Key agricultural outputs include cassava, palm oil, and rice — in substinence and commercial quantity. Anioma is also rich in oil and gas, solid minerals, coal, and other natural resources.
The contemporary political conception of Anioma comprises 100 wards and the 9 local government areas (LGAs) that make up Delta North which include Aniocha North, Aniocha South, Ika North East, Ika South, Ndokwa East, Ndokwa West, Oshimili North, Oshimili South and Ukwuani. 7 out of the 9 local government areas are oil producing. The Anioma population is estimated to be around 2.8 million people following the population growth trajectory, with a population density above 437.5 people per km². Anioma is situated within the West Africa (UTC +1) Time Zone. Anioma landmass is at approximately 6,400 square kilometres, sizeable enough to sustain an independent state infrastructure, agriculture, industry and urban networks. Anioma ranks among Nigeria’s most viable proposed states in terms of economic sustainability, administrative size, and demographic balance.
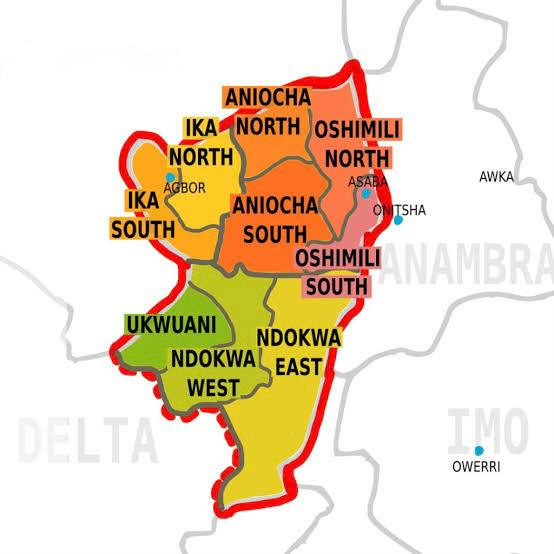
The Main Neighbouring States of Anioma Are
- Kogi State (North)
- Edo State (West)
- Anambra State (East)
- Imo State (Southeast)
- Rivers State (Southeast)
- Bayelsa State (South)
- Delta State (this includes other Delta subregions outside Anioma)
Learn More About Anioma
Explore the history, culture, language, and identity of Anioma through these detailed pages.
